All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. In this case, group 1 how to calculate shares issued consists of 200,000 shares deemed to have been outstanding from 1 January to 31 December. Further, the number of shares used in computing the average is to be weighted by the fraction of the year that the shares were actually outstanding. The inputs you’ll need for this calculation are located on the balance sheet. Get stock recommendations, portfolio guidance, and more from The Motley Fool’s premium services.
Issued Shares: Definition, Example, Vs. Outstanding Shares
The outstanding shares figure is useful to know for an investor that is contemplating buying shares in a company. Dividing the number of shares to be purchased by the number of shares outstanding reveals the percentage of ownership that the investor will have in the business after the shares have been purchased. Moreover, the number of shares outstanding is extremely useful when monitoring how a company conducts its business, as things like stock splits also affect share numbers. An additional metric used alongside shares outstanding is a company’s “float,” which refers to the shares available for investors to buy and sell on the open market. Investors often track changes in outstanding shares as part of their broader analysis when making investment decisions. Understanding the dynamics of outstanding shares is integral to comprehending a company’s financial health and market position.
The market capitalization method

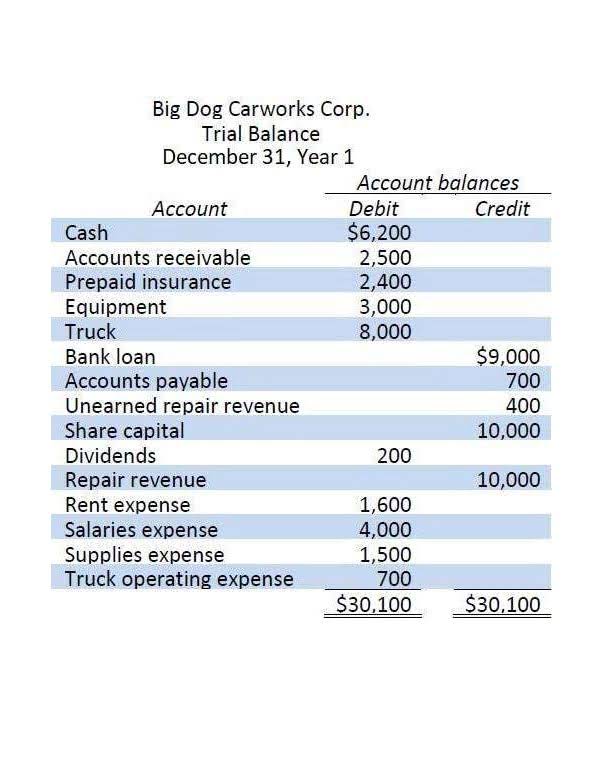
Total shares outstanding decreased from more than 21 billion in 2016 to less than 17 billion in 2020. The tech company spent billions buying back its stock during these years. The number of outstanding shares can be found on a company’s most recent quarterly or annual filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission assets = liabilities + equity (SEC), usually on its balance sheet in the shareholders’ equity section. This « issued » stock can be less than the total authorized, but it can never be more. Outstanding shares include all held by investors, while float excludes restricted shares.

Outstanding Shares Defined
- The weighted average number of outstanding shares in our example would be 150,000 shares.
- Volatility profiles based on trailing-three-year calculations of the standard deviation of service investment returns.
- Shares that a company buys back from the open market, reducing the total number of outstanding shares.
- The result is the number of shares on which the market capitalization number was based.
- Outstanding shares are the total number of shares issued by the company except the ones held in the company treasury.
By contrast, a reverse stock split occurs when a company seeks to elevate its share price. Often, a company does this to meet listing requirements, which often require a minimum share price. Essentially outstanding shares comprise all the shares owned by institutional investors, retail investors, https://www.bookstime.com/ and restricted shares held by insiders. A company’s number of shares outstanding is used to calculate many widely used financial metrics. Market capitalization — share price times number of shares outstanding — and EPS are both computed using a company’s number of outstanding shares.
Papering a Preferred Equity Venture Deal: an Introduction to the NVCA Deal Docs
- If a company buys back its own stock, those repurchased shares are called treasury stock.
- For example, real estate investment trusts are known to issue shares to acquire more properties and grow their business.
- A higher number of outstanding stocks means a more stable company given greater price stability as it takes many more shares traded to create a significant movement in the stock price.
- The term « float » refers to the number of shares available to be traded by the public and excludes any shares held by company executives or the company’s treasury.
- However, there are still some ways you can figure out share counts as an exercise to confirm your understanding of how the company is capitalized.
This can often be found in a company’s financial statements, but is not always readily available — rather, you may see terms like « issued shares » and « treasury shares » instead. Besides, it can be helpful to understand where the numbers you’re looking at came from. Conversely, outstanding stocks will decrease if a firm completes a share buyback or a reverse stock split (consolidating a corporation’s shares according to a predetermined ratio). As a result, it decreases the number of outstanding stocks in the public and increases the amount of treasury shares.